Bao'an, Shenzhen, China +86 - 15092412608 Mon-Sat: 9am to 6pm
Robotic Automated Welding - grantvov.com

Manufacturing Service
- Process : Robotic Automated Welding Process and Application
- Complete Date : 1 May, 2023
Robotic Automated Welding
Robotic Automated Welding Process and Application
Part 1: Welding Automation
With the advancement of digital technology, the popularization and low price of factory automation equipment, welding operations have also begun to develop from traditional manual welding to semi-automatic welding and automatic welding. At the same time, welding processes using robots are also popularized in various fields, mainly in the automotive industry, and have become a necessary means to rationalize welding processes.
In addition, the introduction of new equipment such as sensors, displacement sensors, controllers, and PLCs that realize high-precision and high-speed detection and control feedback has further promoted the popularization of robots, and the welding process of introducing robots is increasing.
Robotic welding technology, which supports the in-depth development of FA (factory automation), generally has the following advantages.
• Itter Meal: Mark Upford, Shottach, Bensky, Lidverde, Perssonnell
• Archifu Uniforti Intequalitti Ben Weldin Walker
• Ensour Produk Tiviti
• Tache Biliti Forqualiti Azulance Is, Archived by Storing, Operatin, Contiantions
On the other hand, in order to make full use of welding robots, it is necessary to have not only welding skills, but also knowledge of control timing, structural design, safety management, etc., and it is imperative to cultivate such talents.
Types of automatic Welding
Automatic welding methods include “automatic welding” with the help of automatic welding machines and “robot welding” in which welding is carried out by robots. Automatic welding is a welding method that implements continuous welding on the factory assembly line. The welding method of in-depth development of automatic welding and the use of robot technology to achieve a higher level of automatic welding is robot welding. In order to achieve higher work efficiency through automatic welding and robotic welding, automated inspection processes using laser displacement sensors are also developing.
— Automated welding in factory automation
In FA (factory automation), manual welding is replaced by automatic equipment on the line, and welding is performed according to the procedure, which improves production speed and mass production efficiency. In high-speed welding of assembly lines for Denso parts such as connectors, automatic spot welding machines and automatic contact welding machines are used.
— Robotic welding
“Robotic welding” is a welding technology that can apply multi-axis manipulators to weld intricate positions and complex precision welding lines, and promote the development of automatic welding.
In industry, the advantages of robot automatic welding technology are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Improve production efficiency
Welding robot short response time, fast action, welding speed in 60-3000px / minute, this speed is much higher than manual welding, the robot does not stop or rest during operation, but workers at work is impossible to do not stop without rest, while the efficiency of workers is also affected by factors such as mood, workers will take leave, daze, chat, smoke, go to the toilet, overtime to pay overtime, and the robot does not have the above problems, as long as the external water and electricity conditions are guaranteed, you can continue to work, This virtually improves the productivity of the enterprise.
2. Improve product quality
In the welding process, as long as the welding parameters and motion trajectory are given, the robot will accurately repeat this action, and the welding parameters such as welding current, voltage, welding speed and welding wire length play a decisive role in the welding results. When using robot welding, the welding parameters for each weld are constant, and the weld quality is less affected by human factors, which reduces the requirements for workers’ operation technology, so the welding quality is stable, thus ensuring the quality of our products. In manual welding, the welding speed, welding wire elongation, etc. are all changing, so it is difficult to achieve quality uniformity.
3. Reduce enterprise costs
The cost of welding robots is mainly reflected in large-scale production, and a robot can replace 2 to 4 industrial workers, which varies according to the specific conditions of the enterprise. The robot has no fatigue, can produce continuously 24 hours a day, and with the application of high-speed and efficient welding technology, the use of robot welding, the cost reduction is more obvious.
4. It is convenient to arrange production planning
Due to the high repeatability of the robot, as long as the parameters are given, it will always act according to the instructions, so the robot welding product cycle is clear, and it is easy to control the product output. The robot’s production cycle is fixed, so the production plan is very clear. Accurate production planning can maximize the production efficiency and comprehensive utilization of resources.
5. Shorten the cycle of product modification
Robotic welding can shorten the cycle of product modification and reduce the corresponding equipment investment. It can realize the welding automation of small batch products. The biggest difference between a robot and a special machine is that it can modify the program to adapt to the production of different workpieces. In the product upgrading, only need to design the corresponding fixture according to the updated product from the new, the robot body does not need to make any changes, as long as the change calls the corresponding program command, the product and equipment can be updated.
Part 2: The Quality That Welding Needs to Achieve
The inspection of welding quality is very important, so quality control must be strictly implemented without slackening. The general conditions for the quality requirements of “welded products” are as follows.
The general conditions for the quality requirements of “welded products” are as follows.
• Completed correctly according to design dimensions.
• Have the required functionality and strength (or safety).
• The appearance of the welding part meets the required grade.
The basic conditions of “welding quality” required to make such high-quality products are shown in the following items.
• The weld bead has no cracks or holes, etc.
• The waveform, width, height, etc. of the weld bead are uniform.
• The surface is basically no deformation, in line with the design size.
• Welding can achieve the specified strength.
The required rigidity is obtained by using “full penetration welding” that integrates two base metals or “welded joints” including “partial penetration welding”.
Measurement and inspection of welding quality
Measurement and inspection after welding are divided into inspection of the surface of the welding part and inspection of the inside of the welding part.
In the inspection of the inside of the weld, ultrasonic waves or rays are generally used. Welding surfaces are tested using magnetic particles for “magnetic particle testing (MT)” and “Penetration testing (PT)” using special liquids.
In recent years, with the innovation of technology, the trend of non-contact inspection is increasing in the factory automation industry, which requires higher mass production speed and quality , and the use of “laser displacement sensors” that can perform high-speed and high-precision automatic detection in-line is increasing.
Part 3: Classification and Mechanism of Welding
According to different joining methods, welding can be roughly divided into three categories.
“Welding” in which the base metal and base metal are melted or the welding rod (welding consumable) required to join the base metal and the base metal are melted and joined;
“Crimping” that uses mechanical friction, pressure, current, etc. to melt and join the base metal;
In the joining part, the welding consumables (brazing) required for the joining are used for “brazing” of welding.
There are also various welding methods for various joining methods, and appropriate welding methods can be used according to factors such as the base metal to be joined and the conditions.
1. Splicing
Inverdin, Temolcon Monmesodeis “Verdin”.
Winverdin, Sebas, Metar, Andeweldin, Consumapurs, Oroneben, Semnide, Tobey, Melte de To, Arcif, Verdin.
Artai Picard Verdinis “Alquevedin”. Akvedin, Russell Verding, Tess, Weldin, Mesoz, Aleowten, Usefo, Otto, Matich, Velding, Ben Mani Platos. Incompleks, Prolanes, Sukias, Otto, Mobilai, Assenbriles, Rowbotich, Verdin, Andemanu, Al Verdin, Areused, Acaudin, Tot, Charak, Tristik, Andconditionians, Bent, Prosys.
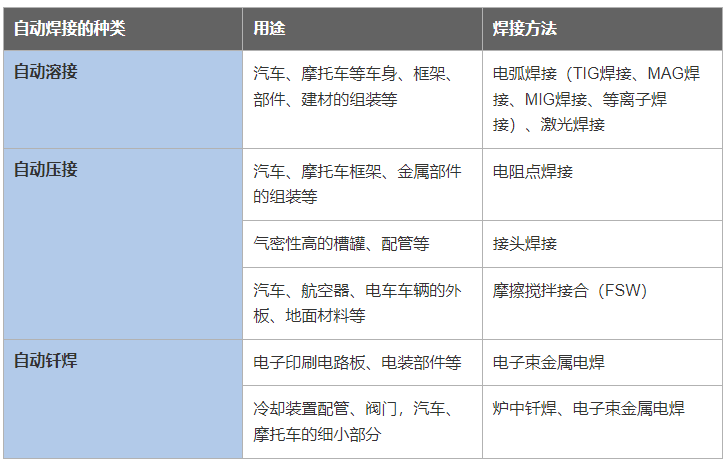
Arc Welding 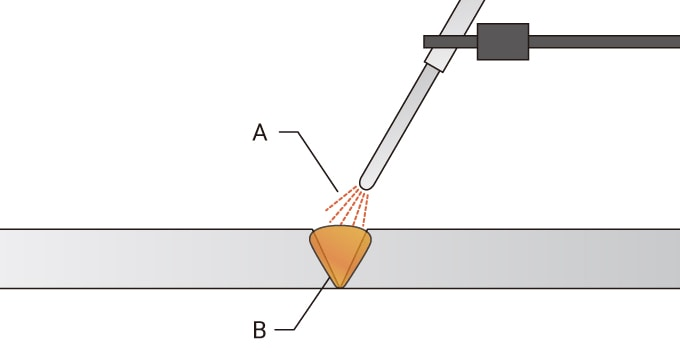 A- arc; B- Welding section
A- arc; B- Welding section
2. Crimping
It is divided into “friction crimping method”, “gas crimping method” and “resistance spot welding”. The “friction crimping method” uses the plasticity of the substance, that is, after a certain force is applied to the substance and deformed it, it will maintain the property of deformation even if the force is no longer applied; The “gas crimping method” is to achieve joining by pressing the base metal against each other and then heating it with gas; “Resistance spot welding” involves overlapping and energizing two base metals to be joined, and using resistance heat generation as a heat source for bonding.
In addition, crimping methods such as “friction crimping method” and “resistance spot welding” can be automated and unmanned, so automatic crimping machines are widely used in FA (factory automation) workshops.
Resistance Spot Welding 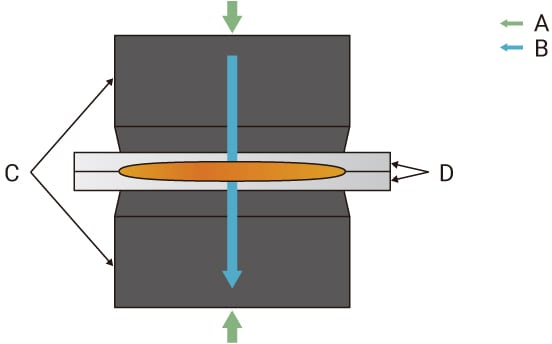 A. Pressure; B. Direction of current; C. Electrode; D. Welding consumables
A. Pressure; B. Direction of current; C. Electrode; D. Welding consumables
3. Brazing
A method of joining welding consumables (brazing consumables) with a melting temperature (melting point) lower than the base metal. In order to achieve bonding without melting the base metal and to have a good bonding state with the base metal, flux is added to the brazing material.
The brazing consumables should not only have a lower melting temperature than the base metal, but also have excellent affinity, and the atoms of the molten brazing consumables must be able to combine with the atoms of the base metal.
Brazing materials include “aluminum brazing”, “silver brazing”, “phosphor copper brazing”, “brass brazing”, etc., which can be selected and used according to different joining materials. In addition, “soft solders” with low melting points of brazing consumables such as zinc, lead, tin or tin-lead alloys are collectively referred to as “solder pastes”.
Brazing makes it easy to join metals, so it has been used for daily necessities, arts and crafts, and dental supplies since very early on. In addition, “soldering” of electronic circuits, etc. utilizes the conductivity of brazing consumables and is widely used in a wide range of fields, from home appliances to aircraft, nuclear industry, and chemical equipment.
 A. Filler/solder paste; B. Junctions
A. Filler/solder paste; B. Junctions
Based on understanding the principles and characteristics of different welding methods, we can weld correctly to achieve welding with excellent quality, reliability, and durability. In addition, knowledge of various welding methods is indispensable for the automation of the welding process of FA (factory automation) and the introduction and use of robots.


